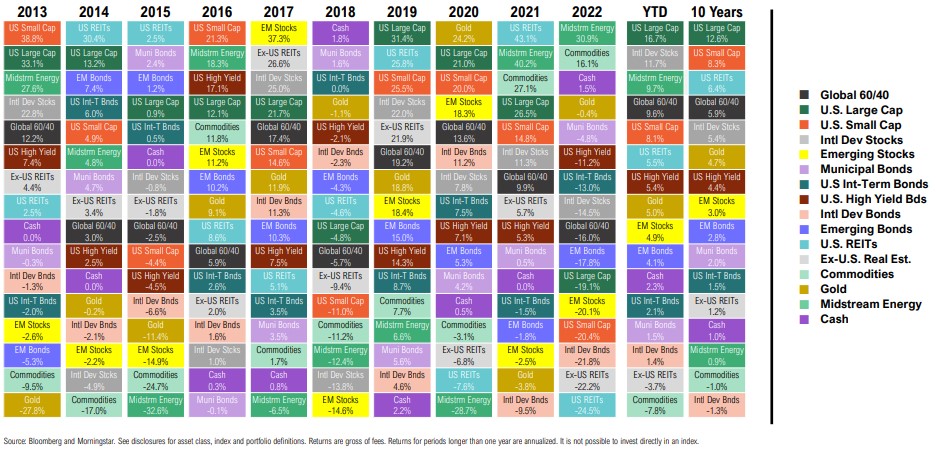
Asset Class Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
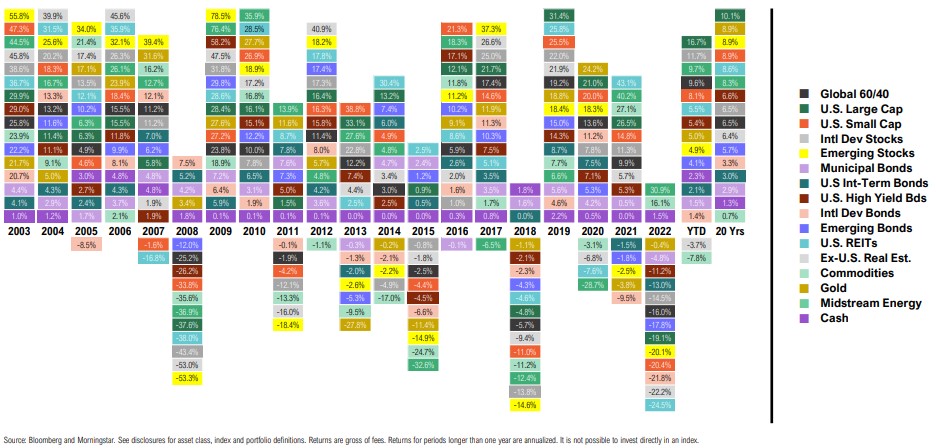
Calendar Decade and Trailing Total Returns

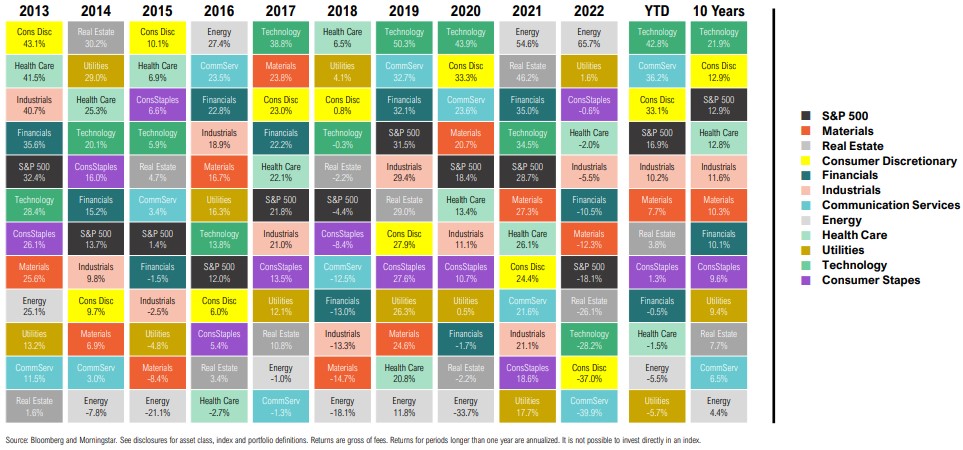
U.S. Equity Sector Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
U.S. Equity Factor Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
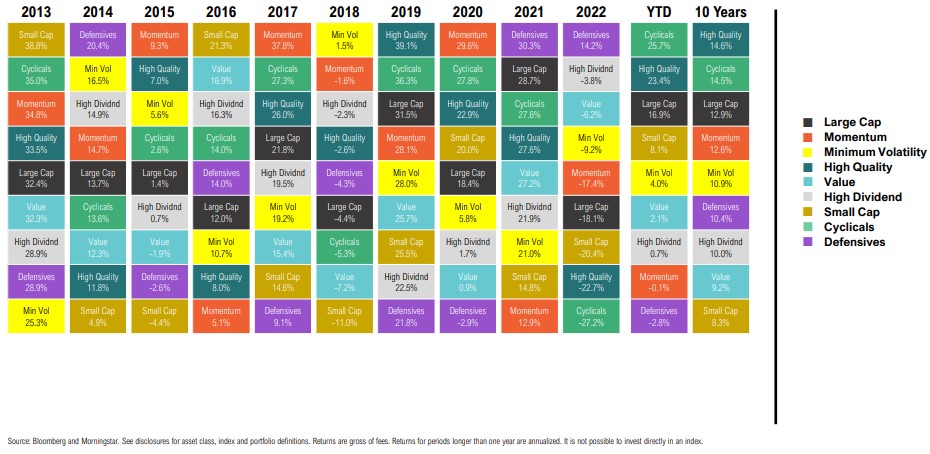
Fixed Income & Credit Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
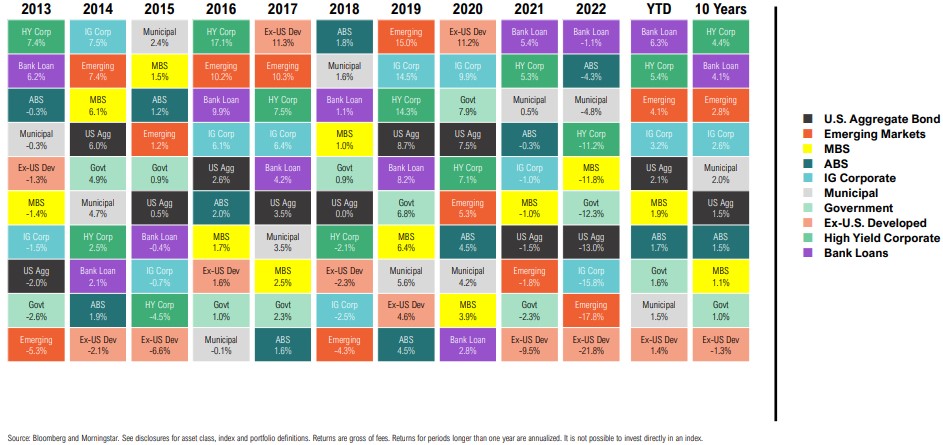
The Most Loved & Hated Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
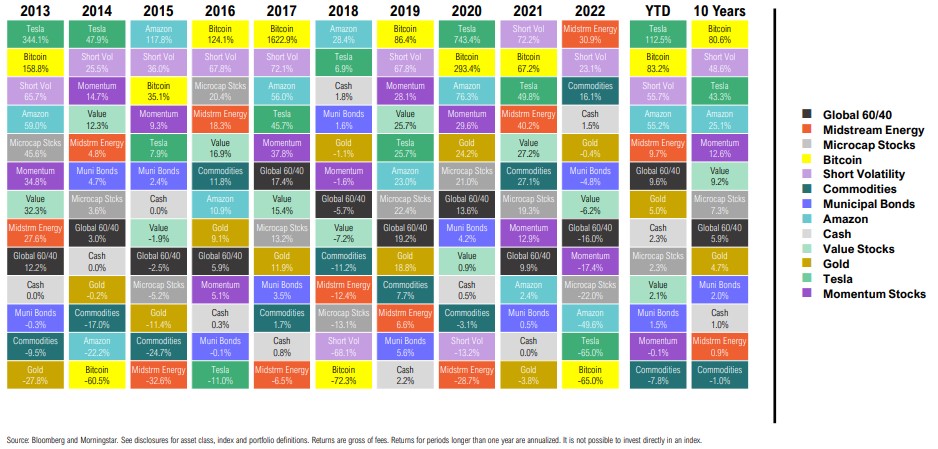
Commodity Futures Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
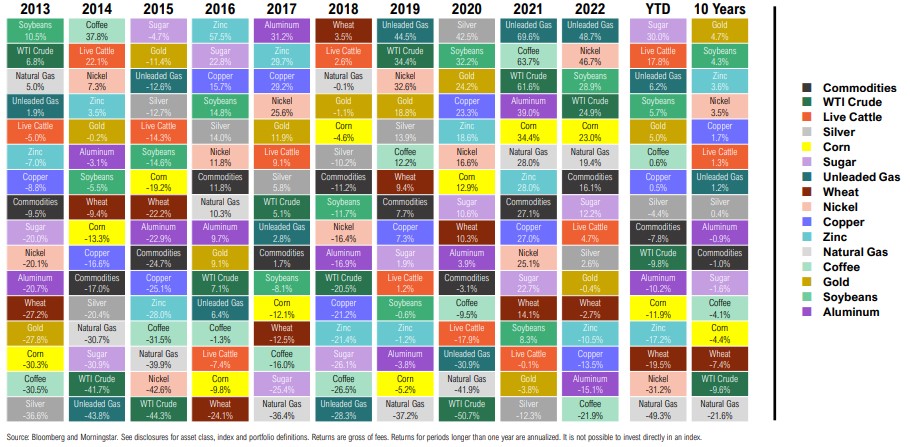
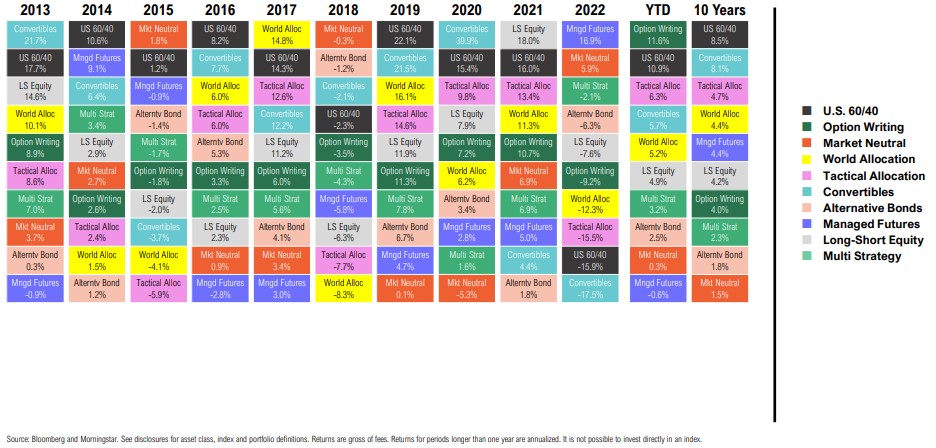
Liquid Alternatives Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing Total Returns
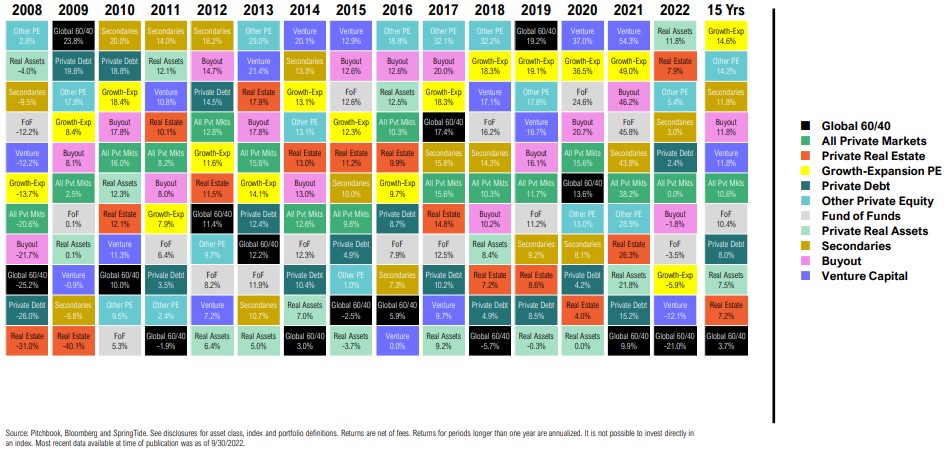
Private Markets Return Quilt
Calendar Year and Trailing IRR
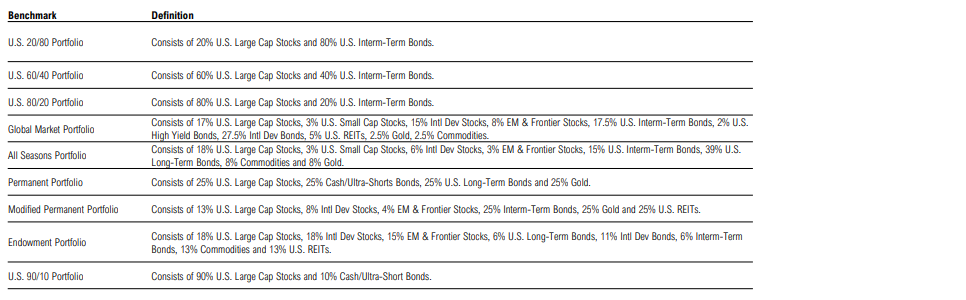
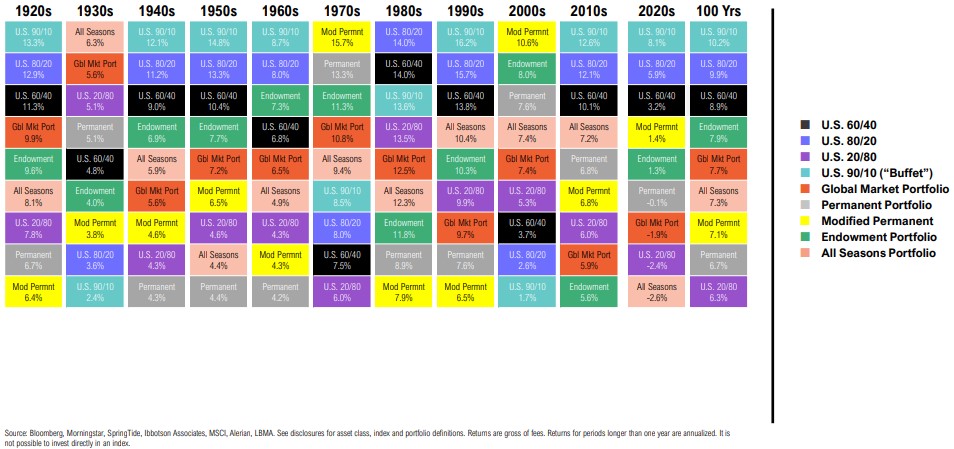
Portfolio Return Quilt
Calendar Decade and Trailing Total Returns
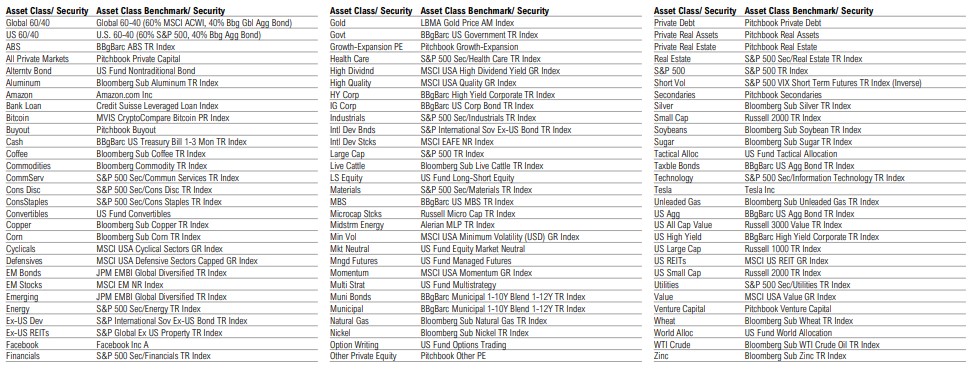
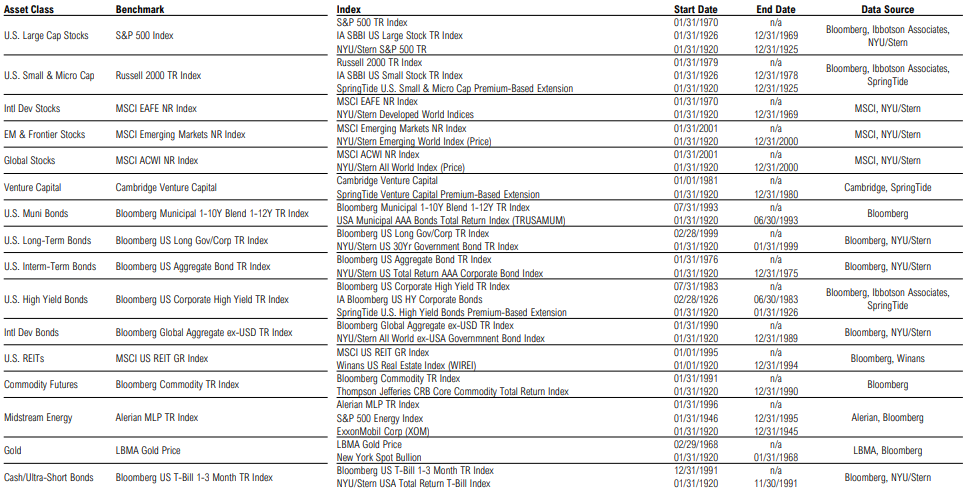
Disclosures & Definitions: Benchmarks
Disclosures & Definitions: Definitions
PRIVATE MARKETS
Buyout Private: Equity funds primarily focus on purchasing at least a controlling percentage of a company’s stock to take over its assets and operations.
Fund of Funds: Funds that take equity positions in other, newly created alternative investment funds.
Growth/Expansion: Private equity funds that make minority (non-control) equity investments.
Other Private Equity: Other private equity includes all private equity that is not specifically buyout or growth/expansion. This includes, but is not limited to: Diversified Private Equity, Mezzanine and Restructuring/Turnaround.
Private Debt: Private debt in general provide various types of debt on private equity transactions and generally includes, but is not limited to, the following: Bridge financing, Credit Trading, Direct Origination or Capital Solutions, Distressed-for-Control, Direct Lending, Distressed Debt, Infrastructure Debt, Real Estate Debt and Venture Debt.
Private Real Assets: Funds that focus on physical assets with intrinsic value due to their substance and natural resources with commodities assets. This includes, but is not limited to: Oil/Gas, Metals & Mining, Timer and Agriculture.
Private Real Estate: Private real estate funds in general are private equity funds that invest in buildings in land. This includes core, core plus, value added, opportunistic and distressed real estate.
Secondaries: Private equity funds that invest in limited partnership interest of funds that have already been raised or directly the purchase of companies from other fund managers.
Venture: Venture Capital funds that invest in new companies with high growth rates. Includes angel funds, early (seed, first, second rounds) stage and later stage (third and later rounds) venture.
LIQUID ALTERNATIVES
Alternative Bonds: Alternative bonds refer to fixed income securities that are not traditional government or corporate bonds. These may include asset-backed securities, high yield bonds, or other types of debt securities that offer unique risk and return characteristics. While alternative bonds may offer the potential for higher yields or diversification benefits, investors should carefully consider the risks associated with these securities before investing.
Convertibles: Convertibles refer to a type of hybrid security that combines elements of both stocks and bonds. Convertible securities typically offer a fixed income stream, like a bond, but also give investors the option to convert the security into shares of the underlying stock at a predetermined price. Convertibles may offer investors the potential for both income and capital appreciation but may also be subject to additional risks and complexities.
Long-Short Equity: Long-short equity refers to an investment strategy that involves taking long positions in securities that are expected to increase in value and short positions in securities that are expected to decrease in value. This strategy may provide the potential for alpha generation and downside protection but may also be subject to additional risks and complexities associated with short selling.
Managed Futures: Managed futures refer to an investment strategy that involves trading futures contracts, such as those based on commodities, currencies, or interest rates, with the goal of generating returns. Managed futures may use a variety of trading techniques, including trend following and counter-trend strategies, and may be subject to additional risks and complexities associated with futures trading.
Market Neutral: Market neutral refers to an investment strategy that aims to generate returns regardless of whether the overall market is up or down. This is achieved by simultaneously taking long and short positions in different securities or asset classes, with the goal of offsetting the impact of market movements. While market neutral strategies can provide diversification benefits, they may also involve additional risks and complexities that investors should be aware of.
Multi-Strategy: Multi-strategy refers to an investment approach that combines multiple investment strategies or styles, such as value, growth, or momentum, in a single portfolio. This may involve a mix of long-only and alternative investment strategies, with the goal of achieving diversification and enhancing risk-adjusted returns. However, investors should be aware that multi-strategy portfolios may involve additional risks and complexities associated with managing multiple investment styles and strategies.
Option Writing: Option writing is an investment strategy that involves selling options contracts, such as calls or puts, on an underlying security with the intention of generating income. However, option writing may also expose investors to potential losses if the market moves against the position. It is important for investors to understand the risks associated with option writing and to carefully consider their investment objectives and risk tolerance before engaging in this strategy.
Tactical Allocation: Tactical allocation refers to an investment strategy that involves making adjustments to a portfolio’s asset allocation based on market conditions or other factors. This may involve shifting investments between different asset classes, such as stocks and bonds, or making changes to individual holdings within a particular asset class. Tactical allocation strategies may be used to capitalize on short-term opportunities or to manage risk in changing market conditions.
World Allocation: World allocation refers to an investment strategy that involves investing in a diversified portfolio of global assets, including stocks, bonds, and other securities, with the goal of achieving long-term growth and income. World allocation strategies may use a variety of approaches, including active and passive management, and may invest in both developed and emerging markets. However, investors should be aware that world allocation strategies may be subject to additional risks associated with international investing.
OTHER
Short Volatility: Short volatility refers to a strategy where investors sell put options to market participants who want to hedge their portfolios against strong, usually negative fluctuations.
Disclosures & Definitions: Asset Classes
Disclosures & Definitions: Portfolios